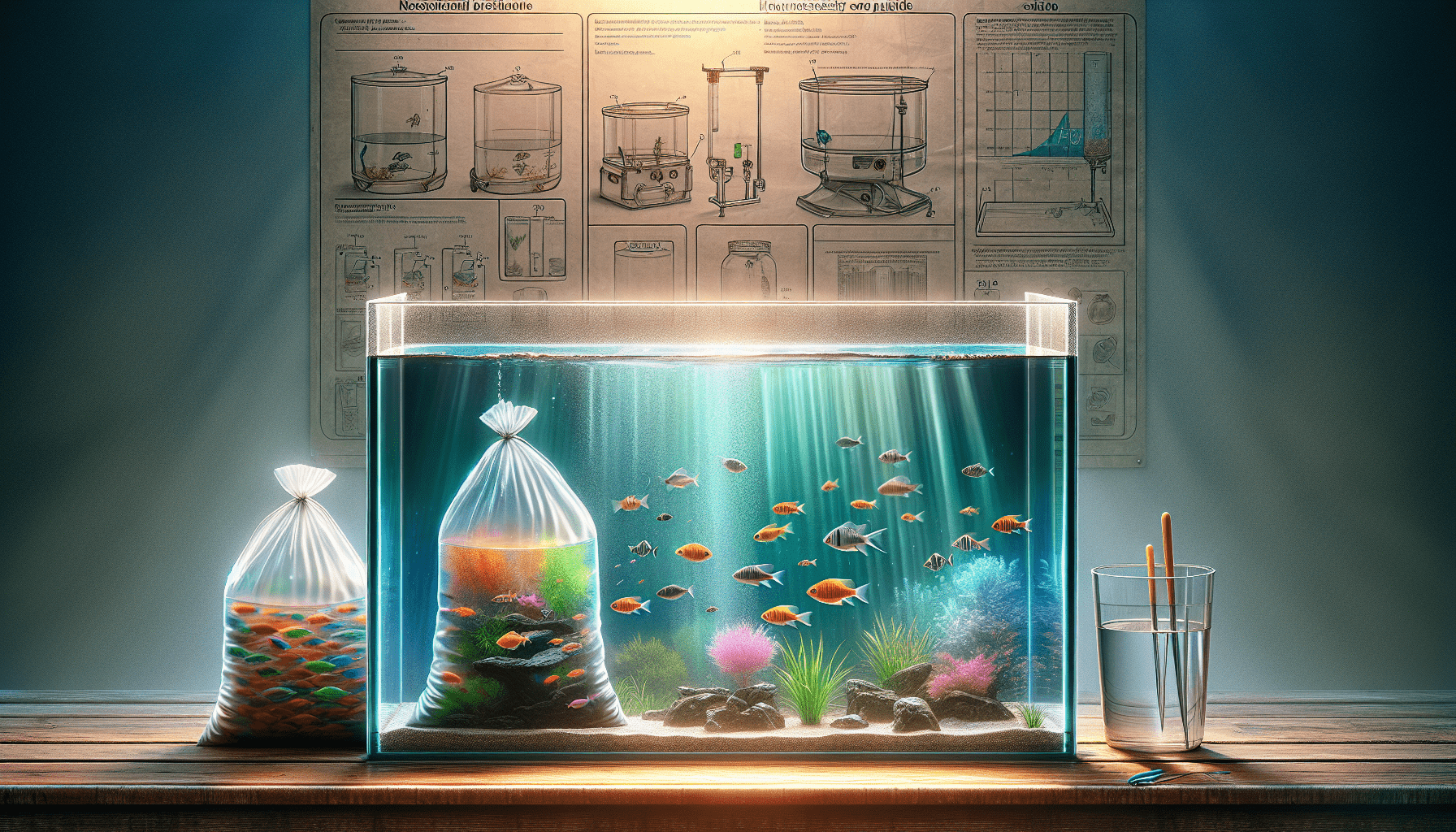
So, you’ve recently set up your brand new aquarium, and now you’re eager to add some vibrant, colorful fish to bring it to life. But hold on just a moment! Before you go rushing to the pet store and filling up your tank with little swimmers, it’s important to understand the crucial process of acclimating your fish to their new environment. This article will guide you through the necessary steps and provide helpful tips to ensure the successful introduction of fish to your new aquarium.

Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is a natural process that occurs in all aquatic environments, including aquariums. It is the biological transformation of nitrogen compounds that fish produce as waste into less harmful forms. This cycle is crucial for maintaining a healthy and balanced aquarium ecosystem.
Why is the nitrogen cycle important for fish?
The nitrogen cycle is of utmost importance for fish as it helps to break down toxic substances, such as ammonia and nitrite, into less harmful nitrates. Fish excrete ammonia through their gills and waste, which can be harmful if not properly processed. By establishing a well-functioning nitrogen cycle, the harmful compounds are effectively converted, providing a safe and stress-free environment for the fish.
How does the nitrogen cycle work in an aquarium?
In an aquarium, the nitrogen cycle begins with the introduction of fish or other organisms that produce waste. The waste breaks down into ammonia, which is highly toxic to fish. However, beneficial bacteria present in the aquarium gradually convert the ammonia into nitrite. Nitrite is also harmful, but another type of bacteria converts it into nitrate, which is relatively less harmful. The nitrates can be removed through regular water changes or utilized as nutrients by aquarium plants. This continuous conversion of toxic compounds is what sustains the nitrogen cycle in an aquarium.
Setting up the New Aquarium
Preparing the aquarium
Before setting up your new aquarium, it’s essential to ensure that you have thoroughly cleaned both the tank and any decorative items. Use a mild detergent or aquarium-safe cleaner to remove any dirt or residue. Rinse everything thoroughly to avoid introducing any potentially harmful substances into the tank.
Choosing the right equipment
Investing in high-quality equipment is vital for the health and well-being of your aquarium inhabitants. When setting up a new aquarium, you’ll need a suitable filter, heater, lighting system, and possibly an air pump depending on the specific requirements of your chosen fish species. Ensure that you select equipment that is appropriate for the size and type of aquarium you plan to maintain.
Adding water to the aquarium
When filling your aquarium with water, it’s crucial to use dechlorinated water. Tap water typically contains chlorine, chloramine, or other chemicals that can harm your fish. Treat the water with a suitable water conditioner to neutralize these chemicals before adding it to the tank. It’s also advisable to match the temperature of the water being added to that of the aquarium to avoid any temperature shocks for your soon-to-be residents.
Filtering the water
A well-functioning filtration system is essential for maintaining a healthy aquarium. The filter removes debris and harmful substances from the water, helping to maintain water quality. There are various types of filters available, such as internal filters, hang-on-back filters, and canister filters. Choose a filter that suits the size of your aquarium and the specific needs of your fish.
Cycling the aquarium
Cycling the aquarium is a crucial step in establishing a healthy nitrogen cycle. The cycling process allows the beneficial bacteria to develop and multiply, ensuring they can effectively convert harmful compounds. There are two primary methods of cycling: fish-in cycling and fishless cycling. Fishless cycling is generally considered to be the safer and more humane option, as it doesn’t subject fish to potentially harmful ammonia and nitrite levels. It involves adding a source of ammonia to the tank, such as pure ammonia or fish food, to feed the growing bacteria. Patience is key during this process, as it typically takes several weeks for the cycle to complete.
Testing Water Parameters
Importance of testing water parameters
Regularly testing the water parameters in your aquarium is crucial for maintaining a healthy environment for your fish. It allows you to monitor for any potential issues and take appropriate action before they become problematic. Testing the water parameters also helps you ensure that the nitrogen cycle is functioning correctly.
pH level
The pH level of your aquarium water indicates its acidity or alkalinity. Different fish species have specific pH requirements, so it’s important to test and maintain the pH within the appropriate range for your chosen fish. A stable pH level is essential for the overall well-being and health of your fish.
Ammonia level
Ammonia is highly toxic to fish and can cause stress, illness, and even death. Regularly testing the ammonia levels in your aquarium is crucial, especially during the initial cycling phase. Ammonia should be kept at zero for a healthy aquarium.
Nitrite level
Nitrite is another harmful compound that can be present in an uncycled aquarium. As the nitrogen cycle progresses, ammonia is converted into nitrite, which is then further processed into nitrate. Testing the nitrite levels allows you to ensure that this conversion is occurring as expected and that the nitrite levels are maintained at a safe level.
Nitrate level
Nitrate is the final product of the nitrogen cycle and is significantly less harmful to fish than ammonia or nitrite. However, high nitrate levels can still be detrimental to fish health, so it’s important to regularly test and keep nitrate levels in check. Performing regular water changes helps to keep nitrate levels under control.
The Cycling Process
Introduction to fishless cycling
Fishless cycling is the process of establishing a healthy nitrogen cycle in your aquarium without subjecting live fish to potentially harmful ammonia and nitrite levels. It involves adding a source of ammonia to the tank, such as pure ammonia or fish food, to feed the growing beneficial bacteria. This process sets the stage for a safe and stable environment for your future fish.
Fish-in cycling vs. fishless cycling
Fish-in cycling, as the name suggests, involves adding fish to the aquarium during the cycling process. While this method was commonly practiced in the past, it is now considered less humane and riskier for the fish. The high ammonia and nitrite levels can stress and harm the fish. Fishless cycling, on the other hand, allows you to establish a stable and safe environment before introducing any fish, ensuring their well-being.
Choosing the cycling method
Choosing the right cycling method depends on your personal preference and willingness to patiently wait for the cycling process to complete. While fishless cycling takes longer, it is widely considered the safer and more humane option. The choice ultimately comes down to prioritizing the health and well-being of your fish.
Adding ammonia to start the cycle
To initiate the cycling process, you will need to add a source of ammonia to feed the beneficial bacteria. This can be done by adding pure ammonia or by adding fish food to the tank. Both methods will result in the production of ammonia as the food breaks down. Following this step, it’s essential to monitor the ammonia levels regularly to ensure that they remain within safe limits for the fishless cycle.
Monitoring ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels
During the cycling process, regular testing of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels will allow you to track the progress of the nitrogen cycle. Monitoring these levels will help ensure that the ammonia and nitrite are being efficiently converted into less harmful nitrate. Consistent monitoring enables you to take appropriate action if levels become unsafe for fish or if the cycling process stalls.
How long does the cycling process take?
The duration of the cycling process can vary depending on several factors, such as the ammonia source, the efficiency of the beneficial bacteria, and the specific conditions of your aquarium. On average, fishless cycling can take four to eight weeks to complete. However, it’s important to remember that the process is not linear, and fluctuations in water parameters are normal. Patience is key during this time as rushing the process can lead to problems down the line.
Testing for Cycling Completion
Ammonia and nitrite levels at zero
A clear indication that the cycling process is complete is when both the ammonia and nitrite levels consistently test at zero. This means that the beneficial bacteria have established themselves in sufficient numbers to convert all ammonia and nitrite into nitrate effectively.
Consistent presence of nitrate
While ammonia and nitrite levels should be zero, the presence of nitrate is expected and indicates a successful nitrogen cycle. Nitrate is far less harmful to fish, and its presence in the water serves as a valuable nutrient for aquarium plants. Regular testing should confirm consistent nitrate readings.
Checking stability
Apart from testing water parameters, observing the stability of the aquarium is essential before introducing fish. The water should appear clear and odorless, and the temperature, pH, and other parameters should remain stable over an extended period. Stability ensures that the aquarium is ready to support and sustain the fish comfortably.
Considering a partial water change
Before adding fish to your newly cycled aquarium, it’s recommended to perform a partial water change. This helps to further lower any existing nitrate levels and ensure optimal water quality for your fish. A 20-30% water change should be sufficient, but ensure that the replacement water is conditioned and at the appropriate temperature to avoid any sudden changes.
Introducing Fish to the Aquarium
Choosing the right fish
When it comes to selecting fish for your aquarium, it’s essential to consider factors such as compatibility, size, and care requirements. Research different species and choose fish that will thrive in the conditions you’ve created in your aquarium. Consider factors such as water parameters, tank size, and the behavior of the fish before making your final decision.
Acclimating the fish
Proper acclimation is crucial to minimize stress and ensure a smooth transition for your new fish. It involves slowly adjusting the water parameters in the bag or container the fish came in to match those in the aquarium. This gradual transition allows the fish to adjust to the new environment without experiencing temperature or pH shocks.
Managing tank size and fish load
It’s important to be mindful of the tank’s size and the number of fish you introduce. Overcrowding can lead to stress, aggression, and poor water quality. Research the adult size of each fish species and plan accordingly to provide adequate space for their natural behavior and growth. Ensuring a suitable fish load helps maintain a stable aquarium environment.
Reasons for gradually adding fish
Adding fish to your aquarium gradually has several benefits. It allows the nitrogen cycle to adjust to the increased bioload, minimizing the risk of ammonia or nitrite spikes. Introducing fish slowly also gives you the opportunity to observe their behavior and health closely, ensuring they are adapting well to their new environment.
Monitoring fish behavior and health
Once your fish are introduced to the aquarium, it’s important to closely monitor their behavior and health. Observe their swimming patterns, appetite, and interactions with other fish. Unusual behavior or signs of illness, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or visible physical abnormalities, should be addressed promptly to ensure the overall well-being of your fish.
Tips for a Successful Transition
Maintaining proper water parameters
Consistently maintaining proper water parameters is crucial for the well-being of your fish. Regularly test the water for pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels to ensure they remain within safe and appropriate ranges. Address any issues promptly by adjusting water conditions or performing necessary maintenance tasks such as partial water changes.
Feeding the fish appropriately
Proper feeding practices are essential for the health of your fish. Feed them a balanced and suitable diet that meets their nutritional needs. Avoid overfeeding, as excess food can lead to poor water quality and various health issues. Feed the fish small amounts at regular intervals and observe their feeding behavior to ensure they are consuming the appropriate amount.
Monitoring and adjusting tank temperature
Maintaining a consistent and appropriate temperature in your aquarium is crucial for the health and well-being of your fish. Monitor the tank temperature regularly using a reliable thermometer. If necessary, adjust the heater to maintain a stable temperature within the recommended range for your specific fish species.
Keeping an eye on ammonia and nitrite levels
Even after the initial cycling process, it’s important to continue monitoring ammonia and nitrite levels regularly. Fluctuations in water quality can occur due to various factors, including overfeeding, overstocking, or equipment malfunctions. Catching any sudden increases in these levels early on can prevent potential harm to your fish.
Performing regular water changes
Regular water changes are essential to maintaining a healthy aquarium. They help remove accumulated nitrates, dilute any other potential toxins, and replenish essential minerals and trace elements. Aim for a weekly water change of around 20-30% of the total tank volume to ensure optimal water quality for your fish.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Adding fish too soon
One of the most common mistakes is adding fish to a new aquarium before the nitrogen cycle is complete. This can lead to stress, illness, and even death for the fish. It’s crucial to be patient and allow the aquarium to properly cycle before introducing any fish.
Overstocking the aquarium
Overstocking the aquarium can lead to numerous issues. A crowded tank can cause stress, aggression, and poor water quality, which can harm the fish. Research the adult size and care requirements of each fish species before deciding on the appropriate number for your aquarium.
Ignoring water testing
Regularly testing the water parameters is crucial for a healthy aquarium. Ignoring water testing can lead to undetected issues such as ammonia or nitrite spikes, which can be harmful to the fish. Make water testing a routine part of aquarium maintenance.
Neglecting regular maintenance
Proper maintenance is vital for a successful aquarium. Neglecting regular maintenance tasks such as water changes, filter cleaning, and removal of debris can lead to deteriorating water quality and increased stress for the fish. Make a schedule and stick to it to ensure a clean and healthy environment for your fish.
Not quarantining new fish
Introducing new fish to an established aquarium without quarantine can be risky. Quarantining new fish before adding them to the main tank allows you to observe their behavior and health in isolation. This helps prevent potential introduction of diseases or parasites to the main aquarium and protects the existing fish population.
Conclusion
Establishing and maintaining a healthy aquarium requires a thorough understanding of the nitrogen cycle and proper aquarium setup. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can provide a safe and welcoming environment for your fish. Remember to be patient, monitor water parameters regularly, and make any necessary adjustments to ensure your fish thrive in their new home. With proper care and attention, you can create a beautiful and thriving aquarium that provides a healthy environment for your fish to flourish.

My name is James Gheen, and I am thrilled to welcome you to Tropical Fish Farmers, the ultimate destination for everything related to tropical fish breeding. As an avid underwater enthusiast, I am dedicated to sharing my knowledge and experience to help you successfully breed and care for tropical fish. Whether you’re a beginner starting your aquarium journey or a seasoned breeder looking to expand your knowledge, my website has something for everyone. Dive into our extensive library of articles, tutorials, and videos covering various topics to enhance your breeding success. Join me in our vibrant community and let’s contribute to responsible fish breeding and conservation efforts together. Discover Tropical Fish Farmers and become part of our global community today.